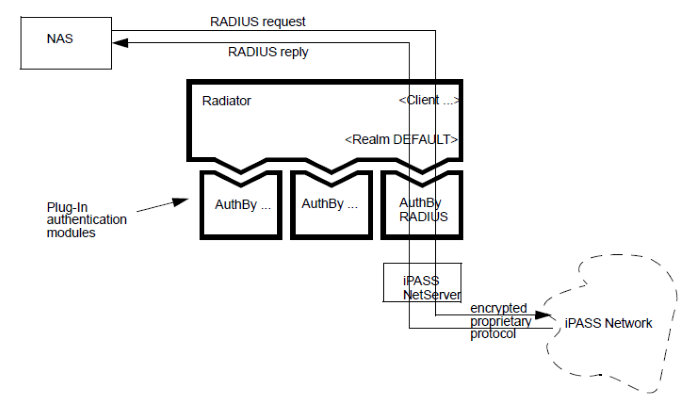
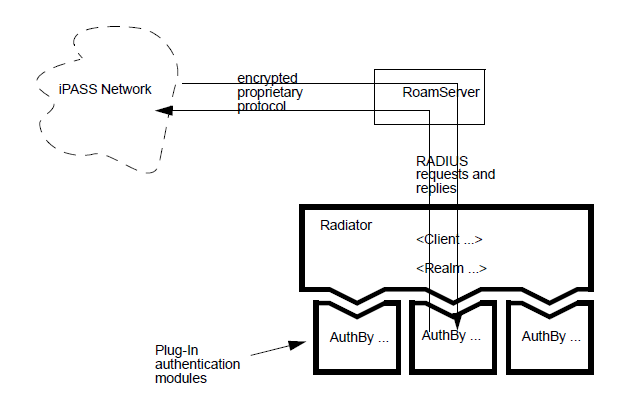
Outbound requests must be proxied to an NetServer, configured
to work with the iPASS system. The NetServer is provided by iPASS. The
NetServer may be run either on the same host as Radiator, or on a
different host. If the NetServer is run on the same host as Radiator, it
must be configured to use different ports to Radiator.
As an
example, here is part of a typical configuration that will handle requests
for local users from a file, and proxy all other realms to an NetServer
running on another host:
# Local realm is handled locally
<Realm my.local.realm>
<AuthBy FILE>
Filename xxxxxx
</AuthBy>
</Realm>
# Al other realms are proxied to NetServer on fred
<Realm DEFAULT>
<AuthBy RADIUS>
Host fred
Secret mysecret
</AuthBy>
</Realm>
Figure 22. Schematic diagram of how iPASS outbound requests are
handled
In order to configure Radiator to handle outbound iPASS
requests, you need to do the following things:
- Enter into a commercial arrangement for iPASS to provide Net
Server access to you. iPASS will provide you with an ISP partner
number.
- Download, install and configure the iPASS software. You will need
to configure both the RoamServer and RADIUS server. This will involve
configuring the package, requesting and receiving an encryption
certificate, and submitting details of your server and realm to iPASS.
Install the package in the normal place
(
/usr/ipass).
- Test the installed iPASS package by using the test programs
provided with it. Make sure it is really working properly before you
go on to the next step.
- Configure Radiator so that all realms that are not handled locally
are forwarded to the NetServer.
- Test Radiator with the radpwtst program to make sure that requests
for non-local realms are forwarded to iPASS.